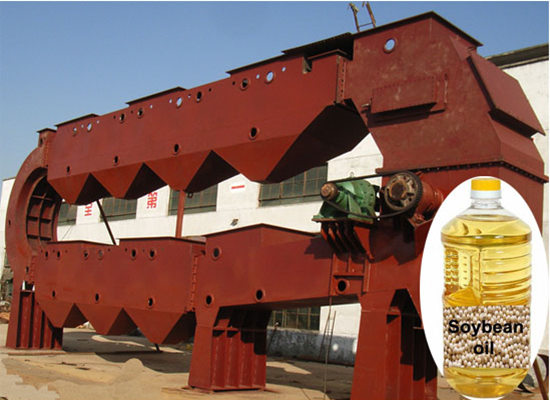
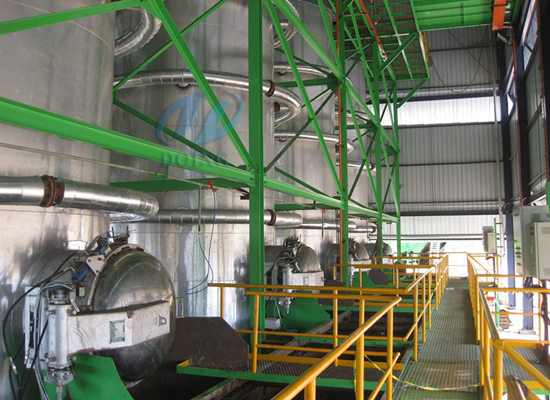
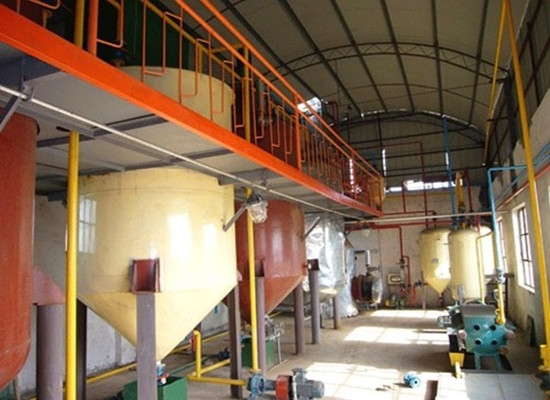
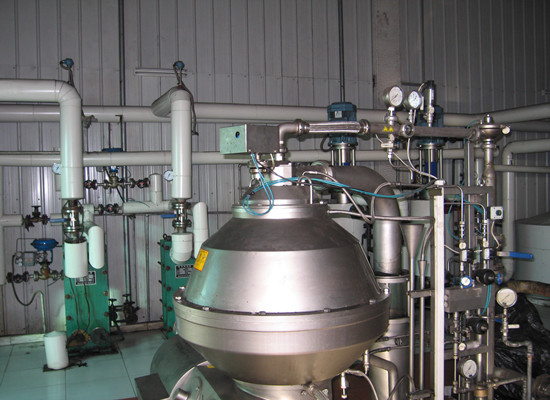
Deacidification process and technology of edible oil
August 13, 2018 15:29/ FAQ/ leave a messageThe refining of edible oils requires a series of refining steps, with the most important being the decrease of the free fatty acid level of the crude oil. The crude edible oil deacidification step is very important for the quality of the final product and has a major impact on the economic feasibility of the whole process. Two processes have been developed for the refining of edible oils and fats, i.e. physical and chemical refining; the decision which process to use depends on the types and qualities of the crude oil to be processed (Fig. 1). The names physical and chemical refining come from the process technology used to remove the free fatty acids (FFA) that are responsible for the oil acidity. Physical refining is a process making use of the lower boiling point of the FFA compared to the boiling point of the triglyceride oil. In chemical or alkaline refining, an alkali is used to neutralise the FFA.
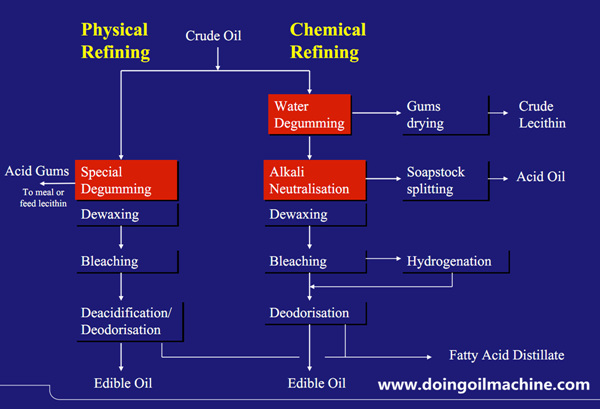
Figure 1:physical refining and chemical refining of edible oil
In addition to the removal of FFA other undesirable non-glyceride materials are also removed. These are mainly:
Phospholipids (gums)
Oxidized products
Metal ions (e.g. iron, copper)
Colour pigments (e.g. gossypol)
Insoluble impurities (e.g. meal fines)
The process steps in chemical refining can be adapted in accordance with the crude oil quality to give a good final oil quality with acceptable oil losses.
Working process of Deacidification process (Neutralization process)
Oil phase free of hydratable gums flows to a Centrifugal mixer after heating in a plate heat exchanger, where it is added with phosphoric acid from acid storage tank by a metering pump. The mixture is further taken to a Centrifugal mixer where it is added with caustic lye from lye solution service tank by a metering pump. The caustic solution circuit is completed with storage tank and recirculation pump. The mixture is then taken to a centrifuge where the non-hydratable gums and soap stock are separated and are pumped out of the system by a pump via a soap collecting tank.
Washing:
Oil free of gums and having traces of soapstock is pumped by a pump through a plate heat exchanger where it is heated by steam. Then it is sent to the Centrifugal mixer to be mixed with water and further centrifuged in a centrifuge for water washing. The washed water is then further sent to the slop oil tank for collection and recovery of escaped neutral oil which is then taken back to the system by a pump.