Degumming process and technology of edible oil
August 13, 2018 14:43/ FAQ/ leave a messageDegumming is the first stage in the edible oil refining process. It is sued to separate the gums, phospholipids, proteins etc. In the degumming process, the gums are precipitated and separated by the centrifugal separation technique. If the gum content in the oil is low, only gum-conditioning is required to be done and there is no need to go for separate degumming process. The degumming can be carried out in the same neutralization vessel.
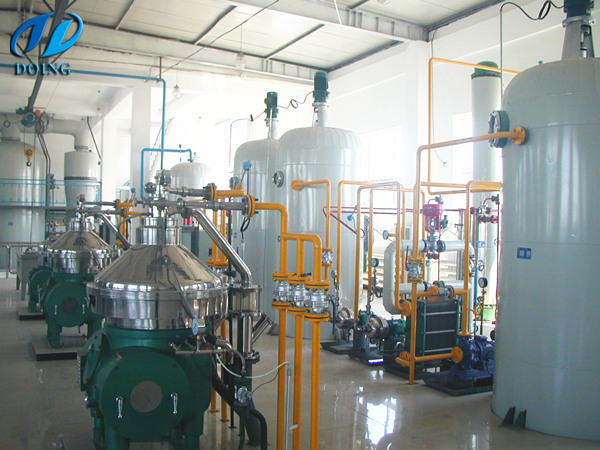

Degumming workshop of edible oil
Purpose of Degumming
Commercial Lecithin production
Prevent crude oil settling during storage or transport
Waste water (prevent acidulation of gums)
Physical Refining
Reduction in neutralisation losses
Gum content of various oils
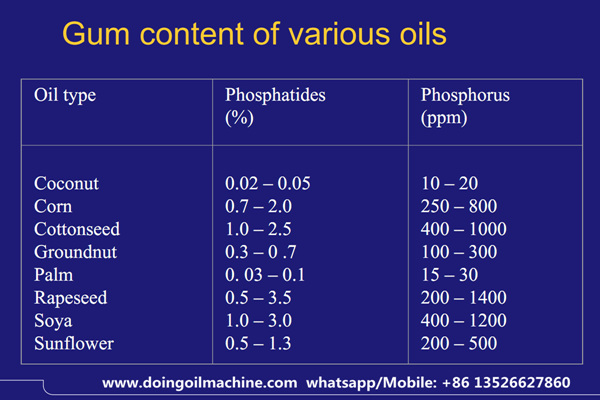
gums content of various oils
Gums——Two main types
– Hydratable Phosphatides - easy to remove
– Non-Hydratable Phosphatides (NHP) - hard to remove from oil
• Some NHP removed with hydratables in water degumming
• requires the use of a acid to convert to hydratable for complete removal
Water Degumming Process Steps
Heat oil to 60 - 70℃
Water addition and mixing
Hydration mixing 30 minutes
Centrifugal separation of hydrated gums
Vacuum drying of degummed oil
Gums - dried for edible lecithin or recombined in meal
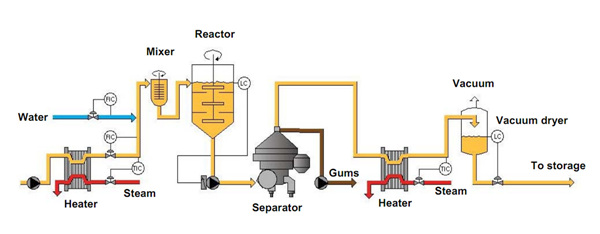
Water degumming process ( Click here to see larger water deguming process flow chart)
Water Degumming——Target Results
Phosphorous in oil - 50 to 200 ppm max.
AI% in dried gums - 65 to 70%
Moisture in dried oil - < 0.1%
Acid Degumming Process Steps
Heat oil to 60 - 70℃
Acid addition and mixing
Hydration mixing 30 minutes
Centrifugal separation of hydrated gums
Vacuum drying of degummed oil
Gums - recombined in meal
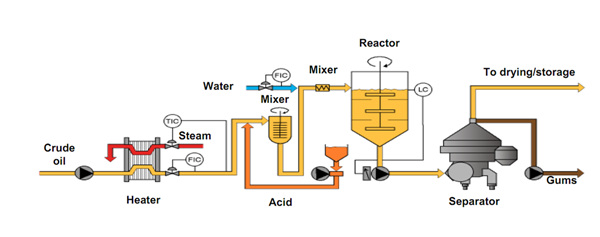
Acid degumming process (Click here to see larger Acid degumming process flow chart)
Acid Degumming——Target Results
Phosphorous in oil - 20 to 50 ppm max.
AI% in dried gums - 65 to 70%
Moisture in dried oil - < 0.1%